# Fonts
- Every piece of text within the elements (
body,h1,p,li, ...) of your website has a font - If you want to change something about the font or text you can select a specific element (using the correct selector) and use the following properties:
| property | example | description |
|---|---|---|
font-family | font-family: Verdana; | font in Verdana |
font-size | font-size: 25px; | size of the font is 25px |
font-style | font-style: italic; | italic font |
font-variant | font-variant: small-caps; | Font in Small Caps |
text-transform | text-transform: capitalize; | first character of every word is uppercase |
text-transform: uppercase; | font in UPPER case | |
text-transform: lowercase; | font in LOWER case | |
font-weight | font-weight: bold; | font in bold |
text-decoration | text-decoration: underline; | font is underlined |
text-decoration: none; | this link is not underlined | |
line-height | line-height: 24px; | height of a text line, fixed value of 24px |
line-height: 1.5; | line-height = font-size * 1.5 | |
text-align | text-align: center; | centers the text |
text-align: right; | aligns the text to the right | |
text-shadow | text-shadow: 2px 2px 8px #ff0000; | adds shadow to the text |
# font-family
- The
font-familyproperty specifies the font of an element - The
font-familyproperty can hold several font names as "fallback" system. If the browser does not support the first font, it tries the next font.
body {
font-family: Verdana, sans-serif;
}
1
2
3
2
3
| EMMET instruction | result |
|---|---|
ff:v + TAB | font-family: Verdana, Geneva, sans-serif; |
ff:ss + TAB | font-family: sans-serif; |
ff:t + TAB | font-family: "Times New Roman", Times, Baskerville, Georgia, serif; |
REMARKS
- To work with fonts in a valid way (without warnings) you need to specify a generic fallback font as the last alternative for the
font-familyproperty
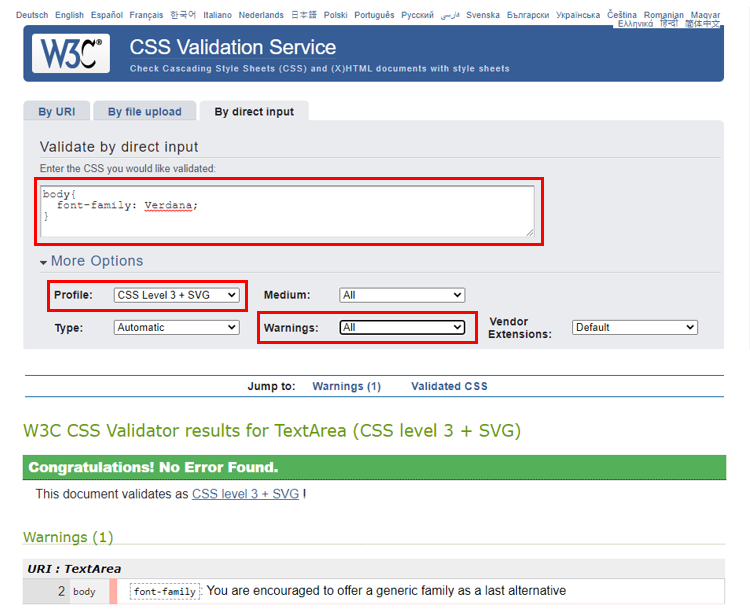
- There are 5 generic fallback fonts which each browsers knows and supports:
serif,sans-serif,cursive,fantasyandmonospacefont-family: Verdana, Geneva, sans-serif;->sans-serifis the generic fallback font
- There are 5 generic fallback fonts which each browsers knows and supports:
- Fonts without serifs ("sans serif") increase both the readability and reading speed of long passages of text
- Fonts with serifs are often used for more elegant/luxury titles
- CSS Font Stack is a good place to read about how to assemble a good collection of fonts (= font stacks)
- Stay away from
Comic Sans MSif you don't want to be the subject of laughter!
# font-size
- The
font-sizeproperty sets the size of a font
h1 {
font-size: 50px;
}
h2 {
font-size: 2rem;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
UNITS OF MEASUREMENT
- There are numerous units of measurement we can use in CSS. In this course we will only use
px(pixels) andrem(relative tofont-sizeof root element):px: commonly used by web developers and designers (Photoshop)- absolute length: fixed
rem- relative length: length is relative to
font-sizeof the root element (which is thehtmlelement, not thebodyelement) - Example: the
font-sizeof theh2element is2rem, which translates to 2 x the browser's root element size (usually16px)
- relative length: length is relative to
| EMMET instruction | result |
|---|---|
fz + TAB | font-size: ; |
fz50 + TAB | font-size: 50px; |
# font-style
- The
font-styleproperty specifies the style of a font- Possible values:
italic,normal(= default)
- Possible values:
p {
font-style: italic;
}
1
2
3
2
3
| EMMET instruction | result |
|---|---|
fs:i + TAB | font-style: italic; |
# font-variant
- The
font-variantproperty specifies whether a text should be displayed in small-caps- Possible values:
small-caps,normal(= default)
- Possible values:
p {
font-variant: small-caps;
}
1
2
3
2
3
| EMMET instruction | result |
|---|---|
fv:sc + TAB | font-variant: small-caps; |
# text-transform
- The
text-transformproperty controls the capitalization of text- Possible values:
uppercase,lowercase,capitalize,none(= default)
- Possible values:
.uppercase {
text-transform: uppercase;
}
.lowercase {
text-transform: lowercase;
}
.capitalize {
text-transform: capitalize; /* first character of every word in uppercase */
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| EMMET instruction | result |
|---|---|
tt:u + TAB | text-transform: uppercase; |
tt:l + TAB | text-transform: lowercase; |
tt:c + TAB | text-transform: capitalize; |
# font-weight
- The
font-weightproperty sets the thickness of text- Possible values:
bold,normal(= default)
- Possible values:
p {
font-weight: bold;
}
1
2
3
2
3
| EMMET instruction | result |
|---|---|
fw:b + TAB | font-weight: bold; |
# text-decoration
- The
text-decorationproperty whether decoration should be added to the text or not
.underline {
text-decoration: underline;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
REMARKS
- Be careful with removing the (default) underlining of link tags!
- According to the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG): If a link is only indicated via color, a contrast ratio of 3:1 between the link color and the surrounding text must be used. This should be accompanied by additional visual cues when hovering over and focusing on the link.
- Reading tips:
| EMMET instruction | result |
|---|---|
td:u + TAB | text-decoration: underline; |
td:n + TAB | text-decoration: none; |
# line-height
- Choosing a correct line height improves the readability of a webpage
- The
line-heightproperty specifies the height of a line
TIP
- To obtain a nice layout, a suitable font is not enough. Also the
line-heighthas to be well-chosen! - Open these examples of good and bad line-heights
- In each of the rectangles you see the same font in combination with a different
line-height - Delete the rectangles (by clicking on them) that you find the least attractive to read, until you have 1 rectangle left
- After that, you will see what most surfers consider to be a good
line-heightand how this ratio came about
- In each of the rectangles you see the same font in combination with a different
p {
line-height: 24px;
}
article p {
line-height: 1.5;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
| EMMET instruction | result |
|---|---|
lh + TAB | line-height: |
lh24px + TAB | line-height: 24px; |
# text-align
- The
text-alignproperty specifies the horizontal alignment of text in an element- Possible values:
left(= default),center,right,justify
- Possible values:
div.center {
text-align: center; /* centers the text */
}
div.right {
text-align: right; /* aligns the text to the right */
}
div.justify {
text-align: justify; /* stretches the spacing so that each text line has an equal width */
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| EMMET instruction | result |
|---|---|
ta + TAB | text-align: left; |
ta:c + TAB | text-align: center; |
ta:r + TAB | text-align: right; |
ta:j + TAB | text-align: justify; |
# text-shadow
- The
text-shadowproperty adds shadow to text- Syntax:
text-shadow: hoff voff blur color;
- Syntax:
| value | required/optional | description |
|---|---|---|
| hoff | required | position of the horizontal shadow; negative values are allowed |
| voff | required | position of the vertical shadow; negative values are allowed |
| blur | optional | blur radius; default value is 0px |
| color | optional | color of the shadow; see Colors |
h1 {
text-shadow: 2px 2px 5px #ff0000;
}
1
2
3
2
3
| EMMET instruction | result |
|---|---|
tsh + TAB | text-shadow: hoff voff blur #000; |
tsh+ + TAB | text-shadow: 0 0 0 #000; |
tsh:r + TAB | text-shadow: h v blur rgb(0, 0, 0); |
tsh:ra + TAB | text-shadow: h v blur rgba(0, 0, 0, .5); |
DESIGN TIP
- Using the RGBA color system (and a partially transparent color) for the shadow usually gives a better/prettier result, especially on colored and non-smooth backgrounds
- It is very important to not overdo text shadows if you want your website to look modern
# All-in-one example
<header>
<h1>HTML Ipsum Presents</h1>
</header>
<article>
<h2>CSS for starters</h2>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Accusamus exercitationem explicabo in laborum
numquam, pariatur porro qui quibusdam sint unde.</p>
<h3>CSS Advanced</h3>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Delectus, facilis?</p>
</article>
<footer>
<h2>Contact</h2>
<p>☎ 014 562310</p>
<p>Tip: <a href="https://www.lipsum.com/">lipsum.com</a></p>
<p>Go to <a href="#">top</a> of page</p>
</footer>
body {
font-family: Verdana, sans-serif;
font-size: 16px;
/*line-height: 24px;*/
line-height: 1.5;
}
h1 {
font-size: 50px;
text-transform: uppercase;
}
h2 {
font-style: italic;
text-align: center;
}
h3 {
font-variant: small-caps;
text-shadow: 0px 0px 4px rgba(250, 100, 50, .47);
}
a {
font-weight: bold;
text-decoration: none;
}
p {
text-align: justify;
}